
Conservative vs. Nonconservative Forces Brilliant Math & Science Wiki
Le Forze Non Conservative e il Loro Impatto sull'Energia Meccanica. A differenza delle forze conservative, le forze non conservative, quali l'attrito e la resistenza dell'aria, influenzano l'energia meccanica di un sistema modificandola. Queste forze, agendo in direzione opposta al movimento, causano una dissipazione di energia cinetica che si.
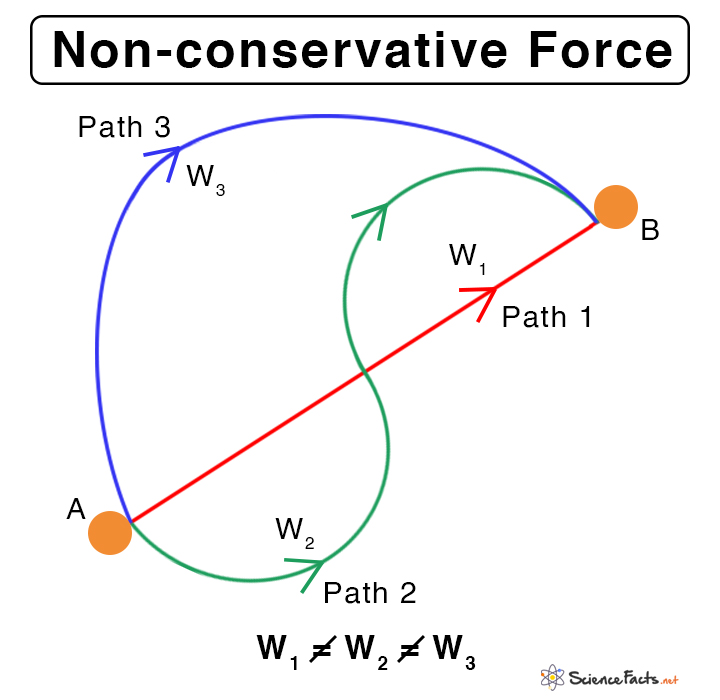
Conservative & Nonconservative Forces Definition & Examples
A non conservative force requires a more complicated mathematical development. One example is friction. The particle or object travels with a finite velocity; whatever its direction, it always leads to dissipation. Another example is the vortex motion of fluids, and the electric field due to induction.
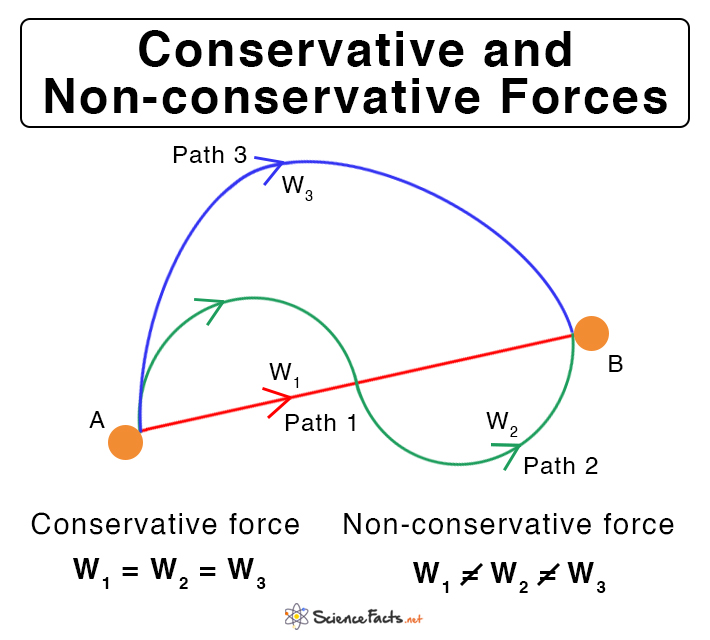
Conservative & Nonconservative Forces Definition & Examples
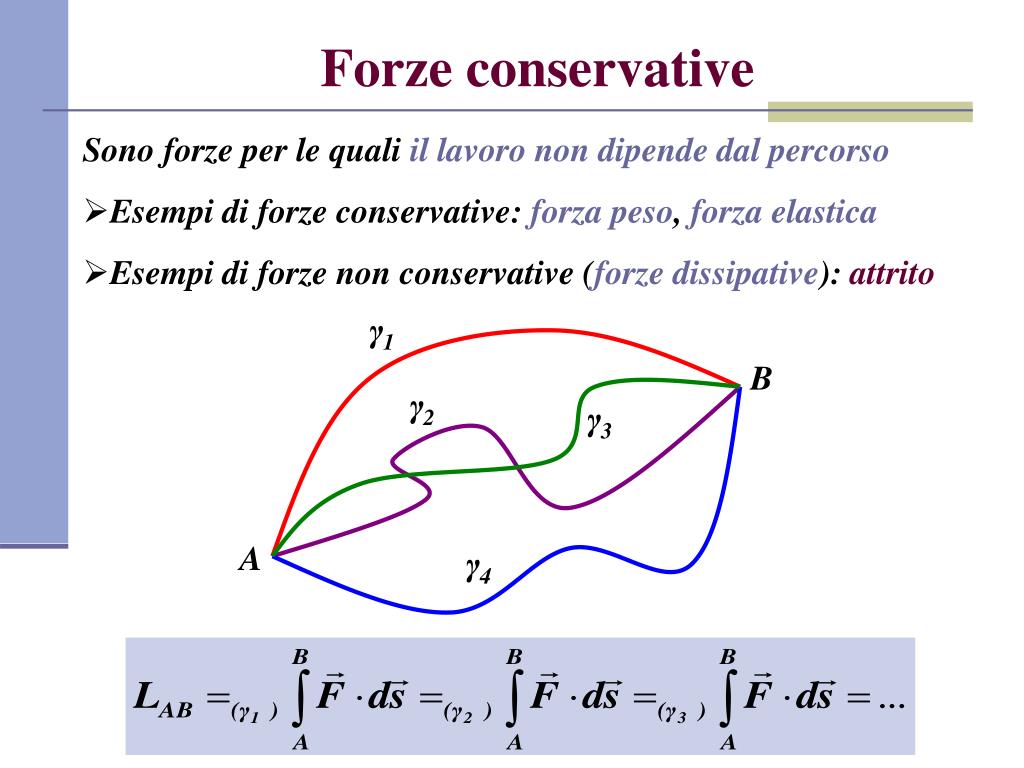
Forze conservative e non conservative . Approfondimento a cura di Marco Ricci. Una forza si dice conservativa quando il lavoro svolto su un percorso che unisce due punti dipende unicamente dai punti iniziale e finale e non dal dettaglio del percorso seguito. Alternativamente, una forza è conservativa quando il lavoro svolto lungo qualsiasi.

Difference Between Conservative And NonConservative Force
If the force is not derived from a potential, then the system is said to be polygenic and the Principle of Least Action does not apply. However, the Euler-Lagrange equations can be derived from d'Alembert Principle.. If we decompose the applied (or specified) forces acting on particle $\alpha$ into monogenic (derived from a potential), $\vec F_\alpha^m$ and polygenic forces, $\vec F_\alpha^p.

Forze conservative ed energia potenziale YouTube
If only these forces act then the mechanical energy of the system remains conserved. Conservative force abides by the law of conservation of energy. Examples of conservative force: Gravitational force, spring force etc. On the other hand, non-conservative forces are those forces which cause a loss of mechanical energy from the system.

Conservative & Nonconservative Forces, & Potential Energy, Mechanical Energy
Forze conservativa e forze non conservative: spiegazione della definizione di forza conservativa e forza non conservativa, con analisi di due esempi: forza p.

PPT Meccanica 8 31 marzo 2011 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4783157
With this definition (1'-3') of a conservative force, then e.g. the Lorentz force and the Coriolis force become conservative forces, while the friction force ${\bf F}=-k {\bf v}$ will stay a non-conservative force, cf. this and this Phys.SE answers. It should be said that there are straightforward generalizations of conditions (1'-3'):

Forze conservative Scuola e cultura
v. t. e. In physics, a conservative force is a force with the property that the total work done by the force in moving a particle between two points is independent of the path taken. [1] Equivalently, if a particle travels in a closed loop, the total work done (the sum of the force acting along the path multiplied by the displacement) by a.

Conservative and Nonconservative Forces YouTube
Forze Conservative e non Sono esempi di forze conservative: La forza gravitazionale (forza peso) La forza elastica (forza di una molla) La forza elettrostatica (attrazione fra cariche), e in generale: tutte le forze centrali, ovverosia forze dipendenti solo dalla distanza dal centro e dirette verso il centro Sono invece non conservative: Le.
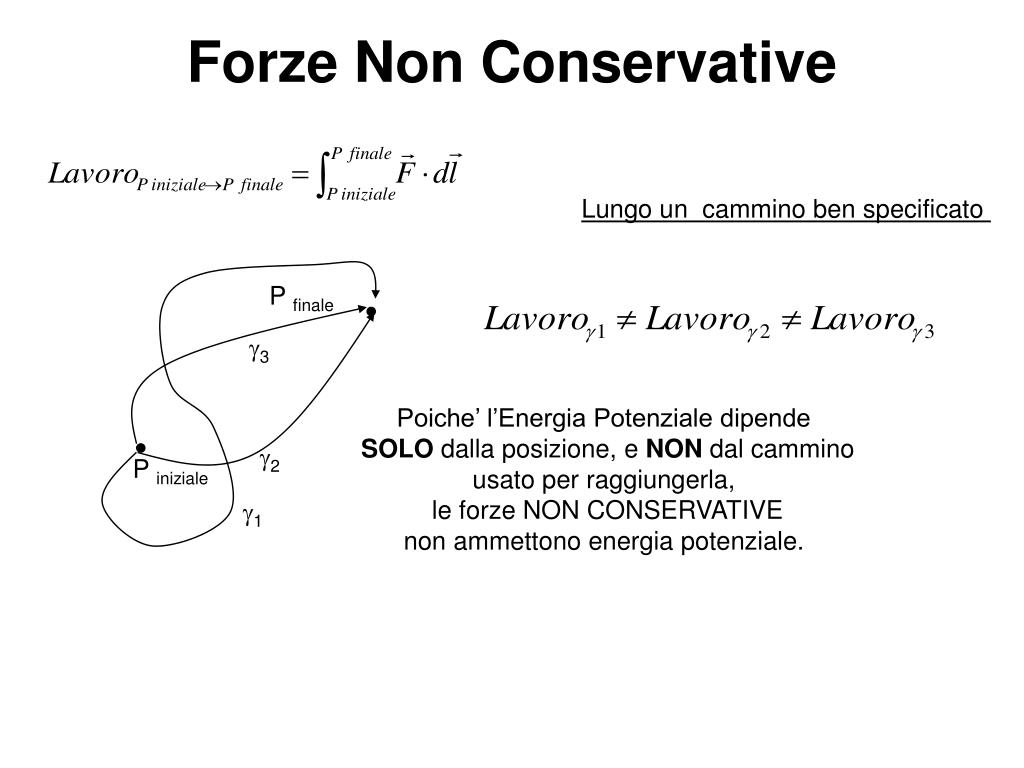
PPT La conservazione dell’energia PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3896022
Forze conservative e forze non conservative #forzeconservativeVideo correlati:Il lavoro https://youtu.be/3W3zv58wQc0La potenza https://youtu.be/D53N_jXdw.

Il lavoro delle forze non conservative YouTube
10.1: Introduction to Nonconservative Systems. A conservative force has the property that the total work done moving between two points is independent of the taken path. That is, a conservative force is time symmetric and can be expressed in terms of the gradient of a scalar potential V. The focus of this chapter is to discuss the origins of.
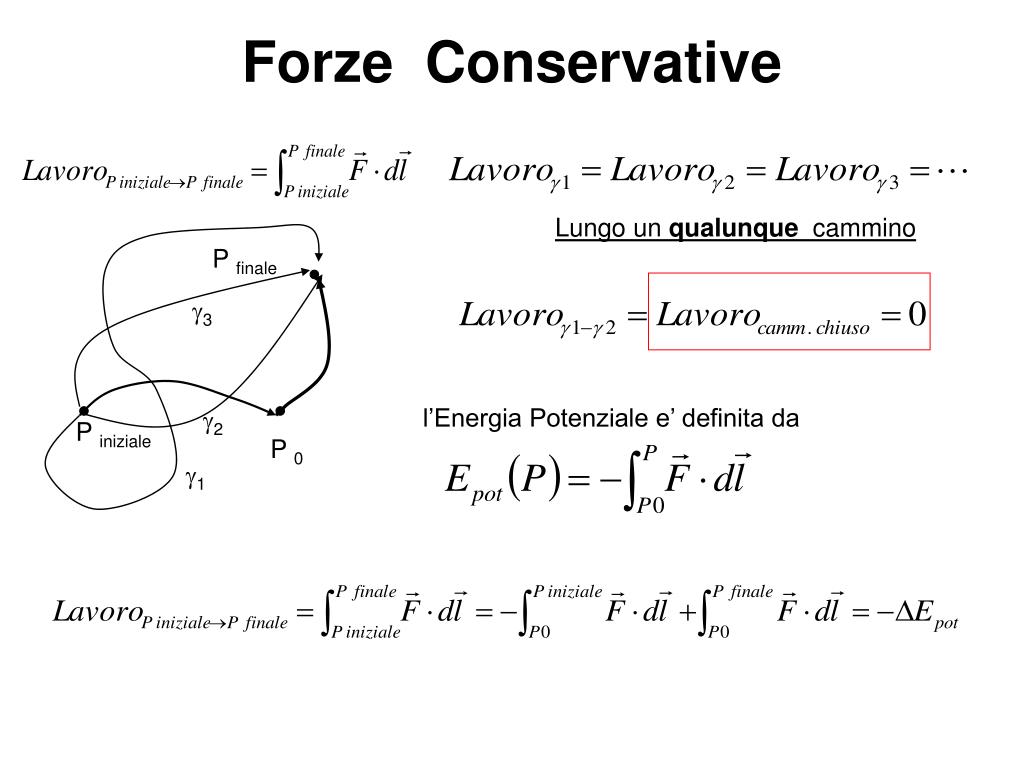
PPT La conservazione dell’energia PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3896022
Ad ogni modo non scoraggiamoci, perché la caratterizzazione delle forze conservative e non conservative discende direttamente dalla definizione, e di volta in volta saremo in grado di capire facilmente se abbiamo a che fare con una forza conservativa oppure no. In soldoni deve accadere ciò che abbiamo visto nel precedente esempio.
PPT Lavoro di una forza costante PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6093116
non-conservative work = -f • x = -µmg x. then, from W non-con = Δ(K + U) = ΔK -µmg x = -mv i 2/2 or x = v i 2 / 2µg Note that the heat from friction is absorbed by both the block and the table; it has already been taken into account in both calculations. Example block starting from rest and sliding down a plane with or without friction.

Difference between Conservative and NonConservative Force Edukar India
Nonconservative Forces and Friction. Forces are either conservative or nonconservative. A nonconservative force is one for which work depends on the path taken. Friction is a good example of a nonconservative force. As illustrated in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\), work done against friction depends on the length of the path between the starting and ending points.

1 La termodinamica Meccanica Forze conservative, principio di conservazione dellenergia
Le forze non conservative possono anche aumentare l'energia totale posseduta da un corpo. Pensate ad una forza esterna applicata ad una massa che si muove a velocità V. La forza, se applicata nella direzione del moto, farà aumentare la sua velocità, quindi la sua energia cinetica, quindi la sua energia totale. Il lavoro compiuto dalle.

5 forze conservative e non YouTube
The work done by a non-conservative force depends on the path taken. Equivalently, a force is conservative if the work it does around any closed path is zero: Wclosed path = ∮E cons⋅ dr = 0. (8.3.2) (8.3.2) W c l o s e d p a t h = ∮ E → c o n s ⋅ d r → = 0. In Equation 8.3.2 8.3.2, we use the notation of a circle in the middle of.
- Da Aeroporto Malta A Sliema
- L Ombra Del Giorno Trama
- Macladin 500 2 Volte Al Giorno
- I Bastardi Di Pizzofalcone Fiori
- Isee 10 000 Euro A Quanto Corrisponde
- Hotel Vitalba Rocca Di Mezzo
- Romanzo Storico Di Scott Ambientato In Inghilterra
- Kate Morton Nuovo Libro 2023
- 20 Franchi Svizzeri In Oro
- Cosa Fare A Procida In Un Giorno
